0506.jpg)
Taipei Veterans General Hospital AI Impact Research Center utilizes Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) to evaluate the impact and economic value of innovative AI technology in healthcare. Due to the broad medical objectives and outcomes designed by innovative AI technology, traditional health economic evaluation methods that use life years or quality-adjusted life years as benefit measures cannot fully reflect their social significance and value. Therefore, the center has designed innovative CEA methods to more comprehensively assess the benefits of AI technology.
Innovative CEA Design of Taipei Veterans General Hospital AI Impact Research Center
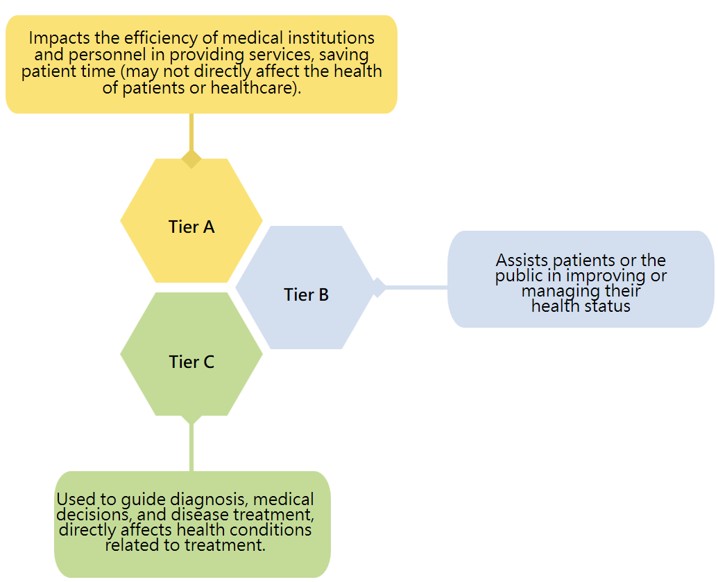
AI Impact Classification:
The center classifies AI impact into three major dimensions (Tier A, B, C), and adopts different cost-benefit analysis methods and techniques based on the impact dimension.
"Taiwan Health Technology Value Index":
- The center has proposed the "Taiwan Health Technology Value Index," which includes life, medical, and social benefits to reflect the multiple dimensions of innovative AI technology impact.
- Through quantitative methods, the benefits and total value of each dimension are estimated to supplement the limitations of traditional CEA methods.
- Social value of benefits:
0506.jpg)
Economic Analysis Models:
- Different economic analysis models are adopted according to AI technology impact classification.
- For example, for Tier C AI technology, decision tree models or Markov models may be used to evaluate their long-term benefits and costs.
Cost-Benefit Assessment Measurements:
- Including Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (ICER), Incremental Net Monetary Benefit (INMB), and Incremental Net Health Benefit (INHB).
Uncertainty in Cost-Benefit Estimation:
- Deterministic (DSA) and Probabilistic (PSA) sensitivity analyses are conducted for parameter uncertainty to estimate the probability of cost-effectiveness.
- For target populations with high heterogeneity, Markov microsimulation models or tolerance interval estimation are used.
- For economic evaluation methods, different economic analysis models are cross-compared for result consistency.
Health Insurance Payment Decision Risk:
- The Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) is estimated to evaluate the opportunity cost of incorrect decisions due to uncertainty, as a reference for the degree of risk impact.
Health Insurance Payment Recommendations:
- For AI technologies that are cost-effective, risk and opportunity costs are provided to recommend risk-adjusted health insurance pricing.
- For AI technologies that are not cost-effective, scenario analysis is used to predict the cost-benefit balance point and estimate the value price that meets cost-effectiveness as a reference for price negotiation or conditional payment.
- Based on the results of budget impact analysis, the affordability of insurance finances and the feasibility of subsequent Price-Volume Agreements (PVA) and other Managed Entry Agreements (MEA) risk-sharing agreements are evaluated.